BIO
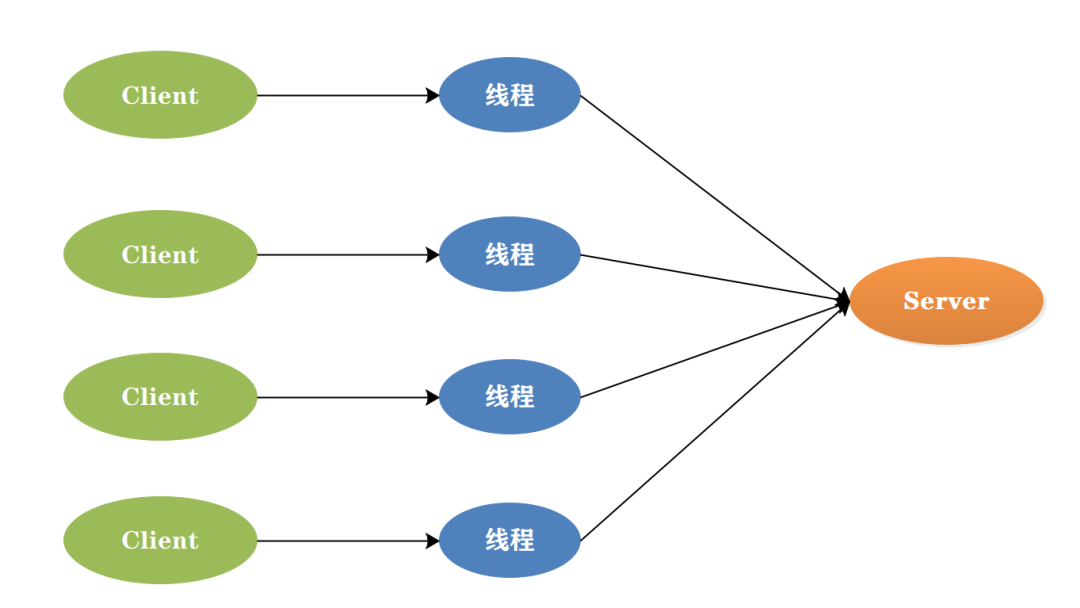
Summary::同步阻塞模型,一个连接一个线程
BIO(Blocking IO) 是最传统的IO模型,也称为同步阻塞IO。它实现的是同步阻塞模型,即服务器实现模式为一个连接一个线程,即客户端有连接请求时服务器端就需要启动一个线程进行处理。如果这个连接不做任何事情会造成不必要的线程开销,并且线程在进行IO操作期间是被阻塞的,无法进行其他任务。在高并发环境下,BIO的性能较差,因为它需要为每个连接创建一个线程,而且线程切换开销较大,不过可以通过线程池机制改善。BIO适合一些简单的、低频的、短连接的通信场景,例如HTTP请求。
优缺点
优点:
- 简单易用: BIO模型的编程方式相对简单,易于理解和使用。
- 可靠性高: 由于阻塞特性,IO操作的结果是可靠的。
缺点: - 阻塞等待: 当一个IO操作被阻塞时,线程会一直等待,无法执行其他任务,导致资源浪费。
- 并发能力有限: 每个连接都需要一个独立的线程,当连接数增加时,线程数量也会增加,造成资源消耗和性能下降。
- 由于I/O操作是同步的,客户端的连接需要等待服务器响应,会降低系统的整体性能。
代码样例
服务端
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class BIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
Socket clientSocket = null;
try {
//创建服务端
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8888);
System.out.println("服务端已启动,等待客户端连接...");
while (true){
// 监听客户端请求,接收不到请求会一直等待
// //accept() 会阻塞(挂起)调用线程,直到一个客户端尝试连接到由 ServerSocket 监听的端口。一旦有客户端连接,accept() 方法就会返回一个新的 Socket 对象,代表与该客户端的连接。
clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();
int port = clientSocket.getPort();
InetAddress inetAddress = clientSocket.getInetAddress();
System.out.println("客户端 "+inetAddress+":"+port+" 连接成功!");
//处理客户端消息
new Thread(new ServerThread(clientSocket)).start();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("客户端连接失败:" + e.getMessage());
} finally {
try {
if (clientSocket != null) {
clientSocket.close();
}
if (serverSocket != null) {
serverSocket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("关闭资源失败:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
/**
* 服务端线程处理类
*/
class ServerThread implements Runnable{
private Socket clientSocket;
public ServerThread(Socket clientSocket) {
this.clientSocket = clientSocket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//获取客户端输入流以便接收客户端数据
try {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(clientSocket.getInputStream()));
//获取客户端输出流以便向客户端发送数据
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(clientSocket.getOutputStream());
int port = clientSocket.getPort();
InetAddress inetAddress = clientSocket.getInetAddress();
String address = inetAddress+":"+port;
String inputLine;
while ((inputLine = in.readLine()) != null) {
//接收客户端消息
System.out.println("客户端"+address+"发来消息:" + inputLine);
//给客户端发送消息
out.println("服务端已接收到消息并回复:"+inputLine);
out.flush();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
客户端
public class BIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket clientSocket = null;
BufferedReader in = null;
PrintWriter out = null;
try {
//绑定服务端ip和端口号
clientSocket = new Socket("localhost", 8888);
System.out.println("连接服务端成功!");
//获取输入流,接收服务端消息
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(clientSocket.getInputStream()));
//获取输出流,给服务端发送消息
out = new PrintWriter(clientSocket.getOutputStream(), true);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true){
System.out.print("给服务端发送消息:");
String msg = scanner.nextLine();
out.println(msg);
String response;
if ((response = in.readLine()) != null) {
//接收服务端响应
System.out.println("服务端响应:" + response);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("连接服务端失败:" + e.getMessage());
} finally {
try {
if (in != null) {
in.close();
}
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
if (clientSocket != null) {
clientSocket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("关闭资源失败:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}